In the world of precision navigation and surveying, RTK GPS networks have become a game-changer. Offering centimeter-level accuracy, these networks are widely used in agriculture, construction, mapping, and autonomous vehicles. But how exactly do corrections in rtk gps networks get delivered in real time? Let’s dive in.
What is an RTK GPS Network?
RTK, or Real-Time Kinematic, is a technique used to enhance the accuracy of standard GPS signals. While traditional GPS provides meter-level accuracy, RTK GPS networks can reduce positioning errors to just a few centimeters. This level of precision is achieved through the use of reference stations and real-time corrections.
An RTK GPS network typically consists of multiple base stations spread over a region. These stations continuously monitor satellite signals and calculate the discrepancies between their known fixed positions and the positions calculated from GPS satellites.
How Corrections Are Delivered
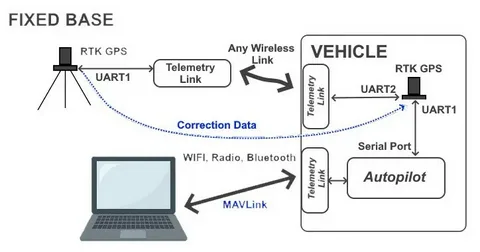
The core of RTK GPS networks lies in the delivery of correction data to mobile receivers in the field, often called rovers. Corrections are transmitted in real time using various methods:
1. Radio Transmission
In traditional setups, base stations broadcast corrections via UHF or VHF radio. The rover receives these signals and applies the correction to its own GPS measurements, ensuring centimeter-level accuracy. This method is widely used in local areas where radio coverage is feasible.
2. Internet-Based Corrections
Modern RTK networks often rely on the internet to deliver corrections. Using protocols such as NTRIP (Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol), correction data from multiple base stations can be transmitted to rovers anywhere within the network’s coverage. This approach is highly scalable and allows for seamless operation across large regions.
3. Cellular Networks
Many RTK systems leverage cellular networks to push corrections in real time. This method combines mobility with high accuracy, making it ideal for applications like autonomous farming equipment or survey teams working in remote areas.
Advantages of Real-Time Corrections
The ability to receive corrections instantly brings numerous benefits:
- Increased Accuracy: Reduces positional errors from meters to centimeters.
- Enhanced Productivity: Eliminates the need for post-processing, saving time and resources.
- Reliable Operations: Ensures consistency in challenging environments where GPS signals might be obstructed.
Conclusion
RTK GPS networks represent a significant leap forward in precision navigation. By delivering real-time corrections through radio, internet, or cellular connections, these networks empower industries to achieve unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. As technology advances, the reach and reliability of RTK GPS networks continue to expand, transforming the way we interact with the world’s geospatial data.